ulnar styloid impaction test|treatment for positive ulnar variance : supplier Jul 10, 2019 Sob o comando do chef Didier, o Bingo Imperatriz criou um cardápio com carpaccio de avestruz com molho de manga. Tudo leve e rápido para comer e jogar ao mesmo .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBlgn.pactosolucoes.com.br é o portal de autenticação da Pacto Soluções, uma empresa que oferece soluções para gestão de academias e negócios fitness. Entre com seu login e .
Ulnar Styloid Impaction Syndrome is a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain secondary to impaction between the ulnar styloid tip and the triquetrum. Diagnosis is made by PA wrist radiographs which reveal positive ulnar variance with subchondral sclerosis of the ulnar .
Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common source of ulnar-sided wrist pain. It is . Jul 10, 2019 Such pain often results from trauma but may stem from nontraumatic conditions. This topic review will provide an overview to acute wrist pain or injury in the adult. Subacute .
Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common source of ulnar-sided wrist pain. It is most common in ulnar positive wrists, whether congenital or acquired, but can occur in ulnar neutral or negative .
Some causes of ulnar wrist pain include: Wrist fractures; Arthritis of the joint(s) between bones; Ulnar impaction syndrome (when the ulna is longer than the radius, which can cause it to “bump into” the smaller wrist . Ulnar impaction syndrome, also referred to as ulnocarpal abutment, is a degenerative condition of the ulnar side of the wrist resulting from excessive load bearing across the ulnar carpus, triangular fibrocartilage .Ulnar impaction syndrome (UIS – sometimes called ulnocarpal abutment) is a condition in which the ulna of the forearm is too long relative to the radius, resulting in excessive loading on the ulnar side of the wrist.
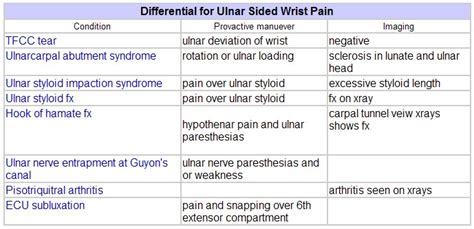
Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common source of ulnar-sided wrist pain. It is most common in ulnar positive wrists, whether congenital or acquired, but can occur in ulnar neutral or negative wrists. Therefore, patients should be .Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common degenerative cause of ulnar wrist pain, which develops because of the effects of force transmission across the ulnocarpal joint.
Background: Ulnar styloid triquetral impaction (USTI), one of many causes of ulnar sided wrist pain, is a pathological entity with clear clinical and radiographic features, distinct and different from the impaction of the ulnar head against the lunate or ulno-carpal impaction (UCI). Pain is ulnar and point-tenderness is present precisely over the ulnar styloid as opposed to the proximal .
Ulnar Styloid Impaction Syndrome Steven M. Topper, MD, Colorado Springs, CO, Michael B. Wood, MD, Rochester, MN, . A provocative test to help distinguish ulnar styloid impaction syndrome from ulnocarpal impaction syn- drome was developed by one of the authors (L. K. R.). It is performed with the patient's elbow resting Ulnar Styloid Triquetral Impaction Test. Several conditions may result in the development of the so-called ulnar styloid triquetrum impaction (USTI or USI) syndrome . For the ulnar styloid process to be able to impact .Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common source of ulnar-sided wrist pain. It is a degenerative condition that occurs secondary to excessive load across the ulnocarpal joint, resulting in a spectrum of pathologic changes and symptoms. It may occur in any wrist but is usually associated with positive ulnar variance, whether congenital or acquired. The diagnosis of ulnar . The diagnosis of this condition is made by radio- graphic evidence of an excessively long ulnar styloid in combination with positive findings on the ulnar styloid impaction test. An excessively long ulnar sty- loid has an USPI greater than 0.21 + 0.07 and/or an overall styloid length greater than 6 mm.
This test uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of the bones and soft tissues. For a wrist MRI, you may be able to insert your arm into a smaller device instead of a whole-body MRI machine. Ultrasound. This simple, noninvasive test can help examine tendons, ligaments and cysts.
ulnar sided wrist pain orthobullets
Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome is a much rarer condition than ulnar impaction syndrome, both of which produces pain on ulnar side of the wrist with subtle differentiating points clinically. . Theulnocarpal stress test in the diagnosis of ulnar-sided wrist pain. Journal Of Bone & Joint Surgery., 22(6), 719–723. CAS Google Scholar Watanabe .
Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome J Hand Surg Am. 1997 Jul;22(4):699-704. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(97)80131-1. . Details of the diagnosis of this condition, including a new provocative test, and operative management are discussed. MeSH terms Adult Carpal Bones / diagnostic imaging Carpal Bones / pathology . Ulnar wrist pain is pain on the side of your wrist opposite the thumb. The ulna is one of two forearm bones. Wrist pain can vary, depending on the cause. Ulnar wrist pain can be linked to many different types of injuries, including problems with .Andrew Hamilton looks at ulnar impaction, one of the more common injuries to affect this region, especially among older athletes. . and fibrocartilage originating from the sigmoid notch on ulnar border of the radius and inserting into the base of the ulnar styloid and fovea of the ulnar head. . a positive ulnocarpal stress test, and .
Create Personal Test Create Group Test . tenderness in the soft spot between the ulnar styloid and flexor carpi ulnaris tendon, between the volar surface of the ulnar head and the pisiform . Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome. ECU tendonitis. Hook of hamate fracture. Ulnar tunnel syndrome. Pisotriquetral arthritis. Treatment.
Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome is characterized by the impaction of the triquetrum against an excessively long ulnar styloid causing chondromalacia, synovitis and ulnar sided wrist pain [1,2,3].The ulnar styloid process is a separate carpal element until it joins to the developing ulnar at around the tenth week of ontogenesis with chondrification usually . Ulnar Impaction Syndrome. Ulnar impaction syndrome is typically a degenerative condition that causes insidious ulnar-sided wrist pain secondary to abutment of the distal end of the ulna or triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) against the ulnar carpus. The pain is usually made worse with pronation of the forearm and ulnar deviation at the wrist.Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common degenerative cause of ulnar wrist pain, which develops because of the effects of force transmission across the ulnocarpal joint. Although the pathologic changes and clinical syndrome most typically . Ulnar styloid impaction is characterized by the impaction of the triquetrum against the ulnar styloid causing chondromalacia, synovitis and ulnar-sided wrist pain. . Ulnar styloid provocation test as described by Ruby (1997): Patient’s forearm rests on table in neutral rotation with wrist in full extension, brought by examiner into full .
Ulnar Styloid Impaction Syndrome . ulnar deviation and carpal supination. pathoanatomy. osseous. . Watson test. when deviating from ulnar to radial, pressure over volar aspect of scaphoid subluxates the scaphoid . Ulnar-sided wrist pain is a common cause of upper extremity disability. Presentation can vary from acute traumatic injuries to chronic degenerative conditions. Because of its overlapping anatomy, complex differential diagnosis, and varied treatment outcomes, the ulnar side of the wrist has been referred to as the “black box” of the wrist, and its pathology has . Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome refers to impaction between the ulnar styloid and the triquetrum bone which results from repetitive or acute forced ulnar deviation and dorsal flexion of the wrist . It may occur due to morphologic variations (such as elongation, radial deviation, or enlargement) or pathologic conditions (nonunion, malunion, or .
IMPORTANT POINTS Ulnar impaction syndrome results from abnormal force distribution across the ulnar carpus. . Nakamura’s ulnar stress test is performed by ulnarly deviating the pronated wrist while axially loading, flexing, and extending the wrist. . should begin 1 to 2 cm proximal to the ulnar styloid and continue proximally for 15 cm .The development of UIS leads to the progressive degeneration and increased abutment of the distal ulna or TFCC against the ulnar carpus. Although any athlete can suffer from this condition, gymnasts, boxers, racquet and stick sport athletes are particularly at risk, with symptoms of pain particularly occurring during wrist rotation. This combined injury (ulnar styloid and distal radius fractures) can elevate the risk of DRUJ instability (10–19%) [7, 23]. Lindau, 2005 established a relationship between ulnar styloid base fractures and injuries to the TFCC, the primary soft tissue stabilizer of the DRUJ. The TFCC’s anatomical insertion site is the ulnar fovea, located at .Ulnocarpal impaction syndrome is a common cause for ulnarsided wrist pain caused by an abutment between the ulnar head and the lunotriquetral complex. This pain is typically triggered by load bearing and rotation of the forearm. Radiographic examination is often associated with positive ulnar variance and cysts in the lunate, edema of the ulnoproximal lunate is shown in .
The most common upper extremity fractures presenting to the emergency department are distal ulna and radius injuries.[1] First responders, physicians, and support staff must understand how to manage these injuries.[2] The appropriate treatment for a distal ulna fracture is typically surgical correction of the radius first. Once the radius is stable, most distal . The ulnar snuffbox test is performed by applying radial pressure in the sulcus between the ECU and the FCU distal to the ulnar head. . Some authors have suggested that dorsal cortical fractures can be produced from avulsion fractures or impaction of the ulnar styloid when the wrist is forcibly dorsiflexed and ulnarly deviated. Isolated . Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome involves repetitive friction between an excessively long ulnar styloid and the carpus, resulting in chondromalacia, synovitis, and pain. . The scaphoid shift test and fovea test were negative, and the distal radioulnar joint was stable. The patient was instructed to wear a splint for 4 weeks; upon follow-up .The ulnar styloid is a projection of the distal ulna which functions as an attachment for several structures including the extensor carpi ulnaris . Ulnocarpal stress test: Pain: Ulnocarpal impaction, central TFCC tear: Press test: Pain: Ulnar-sided wrist pain, possible TFCC: Hook of hamate pull test: Pain:
ulnar positivity
WEBCurso Livre . Metodologia: O Curso Gratuito Online de Microsoft Project deverá ser desenvolvido de forma autônoma e exigirá que você estude cada Módulo, a fim de ter .
ulnar styloid impaction test|treatment for positive ulnar variance